Designing an effective wildfire protection sprinkler system for remote buildings requires accurate calculations of flow (GPM) and pressure (PSI) to ensure water is delivered efficiently and consistently to each sprinkler.
Key Factors to Calculate
Sprinkler Flow and Pressure Requirements
- Flow: 2-5 GPM on most spriklers. Note: the Wasp roof sprinklers are designed for very low flow of 1.6GPM to operate off garden hose outlets, max 3 sprinklers per outlet.
- Pressure: 20-60 PSI
- Sprinkler Loss: Assume ~5 PSI per sprinkler head (internal friction loss)
Friction Loss in Supply Lines
- 3/4” type K copper tubing (100 ft): ~5 PSI loss per sprinkler line
- 3/4” garden hose (100 ft): ~10-15 PSI loss (varies)
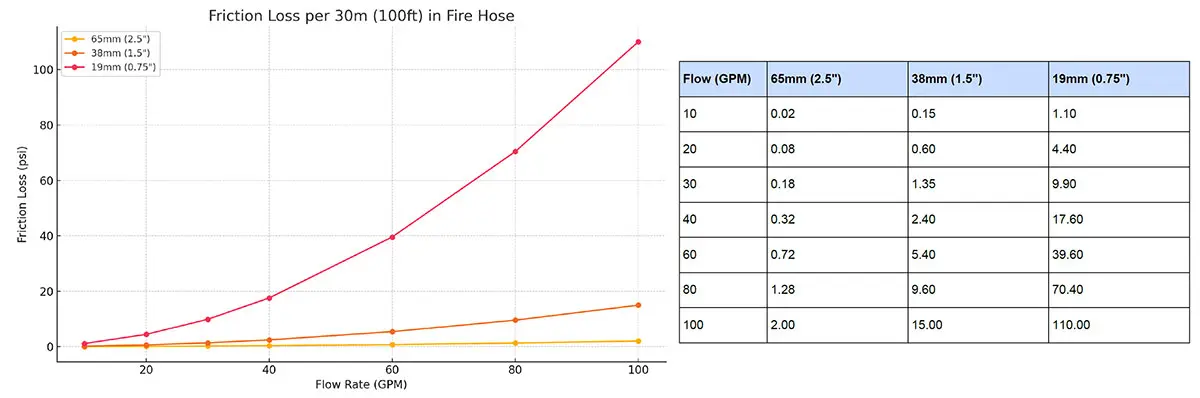
- 1.5” or 2.5” fire hose: Minimal loss over short distances
The equation for Friction Loss (FL) = C × (GPM²) × (L ÷ 100) is used in fire hydraulics to calculate the friction loss in a hose due to water flow. Here’s what each variable represents:
- FL = Friction Loss (in psi)
- C = Friction loss coefficient, which depends on the hose diameter and type
- GPM = Flow rate in gallons per minute
- L = Length of hose (in feet)
Explanation:
- The term GPM² means the friction loss increases exponentially with the flow rate.
- The L ÷ 100 part normalizes the hose length to 100-foot sections.
- The C factor accounts for hose characteristics—smaller diameter hoses and rougher interiors have higher C values.
This formula is essential for determining pressure needs in firefighting.
Elevation Pressure Loss
Loss: ~5 PSI per 10 feet of vertical lift (1 story)
Example: A building 20 ft higher than your pump will need 10 PSI just to overcome gravity.
Step-by-Step Calculation Example
Protecting 4 sprinklers (3 GPM each) on a rooftop 20 ft above the water source:
- Total Flow: 4 x 3 GPM = 12 GPM
- Pressure per Line: 30 PSI (sprinkler) + 5 PSI (friction) + 10 PSI (elevation) = 45 PSI
- Pump Requirement: At least 12 GPM @ 45 PSI
Design Tips
- Use larger diameter hoses (e.g., 1.5”) for trunk lines
- Split the system into zones, using a manifold, if using more than 4-6 sprinklers
- Ensure pump maintains both flow and pressure under load
- Use check valves and regulators for elevation control
Helpful Tools
- Friction Loss Calculators
- Manufacturer Pump Curve Charts
- Flow meters for testing

Choose length, size, and threads.

Designed for high pressure centrifugal pumps

For the foot valve strainer.

Determine size needed from 6hp to 20hp. Review performance flow charts to determine suction inlet requirements.

Determine size required. We recommend quick connects.

Recommend 38mm to get close to the sprinklers, but for very long runs we recommend 65mm hose.

Use to break away from 38mm hose to patrol hose which supplies the sprinklers.

Choose roof-top, tripod, or offset sprinklers as required.